What is an Pilonidal Sinus?
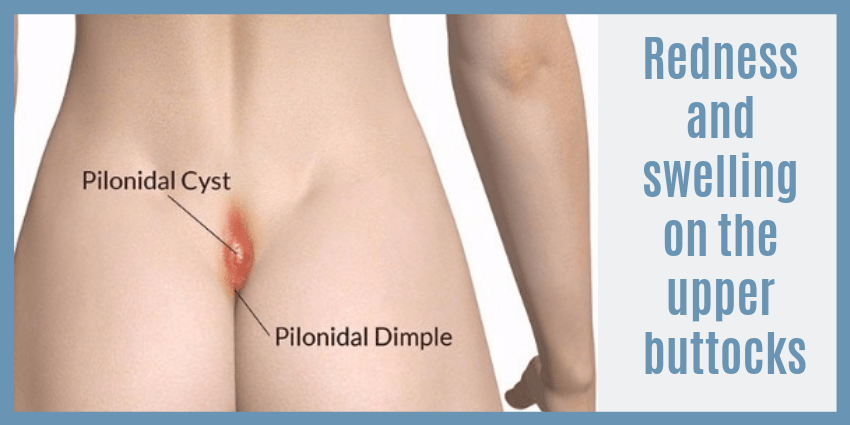
Pilonidal sinus is a small hole or a tunnel in the skin which gets filled with pus or fluids. It is a kind of an infection that occurs at the upper part of the cleft of the buttocks. Pilonidal sinus is a sinus tract or a small tunnel that may originate from the site of infection to the open surface of the skin.
Pilonidal Sinus is also referred to as Jeep Drivers disease. This is because during the Second World War many jeep drivers got this condition because of the nature of their occupation which required them to drive for long hours. The condition of the upholstery those days also aggravated and caused Pilonidal Sinus.
What are the causes of Pilonidal Sinus?
- Although the cause for Pilonidal sinus is still a controversial subject, the most widely accepted theory is that the loose hairs that penetrate into the skin can cause Pilonidal sinus.
- Long sitting hours, tight clothing, cycling and other activities increase friction, heat and pressure in the bottom region. This causes the hairs in the upper buttocks region to bend backwards, penetrate the skin and grow inwards.
- This inward growing hair is treated as foreign particles by our body and hence the body reacts to it by forming a cyst around the hair follicle. Later the hair tunnel is filled with fluid and pus. If left unchecked an abscess may be formed and infection happens as a result.
What are the symptoms of Pilonidal Sinus?
- If the Pilonidal cyst gets infected, the patient may present with severe pain. This pain is likely to aggravate while sitting and squatting. The infection can also induce fever. This is a normal reaction as the body fights infection.
- A visible redness with swelling around the infected area can be seen.
- Blood and foul smelling puss might be discharged from the outer opening of the tunnel.
- In the presence of an infection the patient might present with high grade fever also.
- The substances from the cyst can drain out through the Pilonidal sinus. If the pilonidal cyst gets infected the abscess from this pilonidal cyst can be extremely painful.
Who are at the risk of getting Pilonidal Sinus?
- Pilonidal Sinus more commonly affects young males. Men with hair in the upper buttocks region carry more risk.
- People with jobs that require them to be seated for a long time are prone to get Pilonidal Sinus.
- Obesity and poor hygiene are also associated factors for Pilonidal Sinus.
How is Pilonidal Sinus Diagnosed?
- A general physical Examination is performed by the gastric surgeon.
- If the infection is severe, a blood test is also recommended.
- If surgery has been opted MRI is suggested to pinpoint the accuracy of the sinus tract, its length, depth and the branches if any. MRI also helps in ruling out any other neurological congenital anomalies.
What are the non-surgical treatments for Pilonidal Sinus?
Non-Surgical treatment can be done only if the cyst is yet to get infected. Some of the common non-surgical treatments include
- In the initial stages of Pilonidal Sinus, the infection is managed by delivering doses of antibiotic to the patient.
- Pain killers and Anti-inflammatory drugs may also be prescribed by the doctor.
- Sitz baths, sitting in a tub of warm water up to the hips, can relieve the pain and swelling.
- Vitamin C, vitamin A and zinc supplements can help in the healing process.
- Chemical depilatory’s can be used to remove hair from the skin. This method can very well serve as a precautionary method for men with a hairy bottom.
However, it should be noted that since the hair and other debris are still lying in the pilonidal sinus so formed, they can be removed only through surgery.
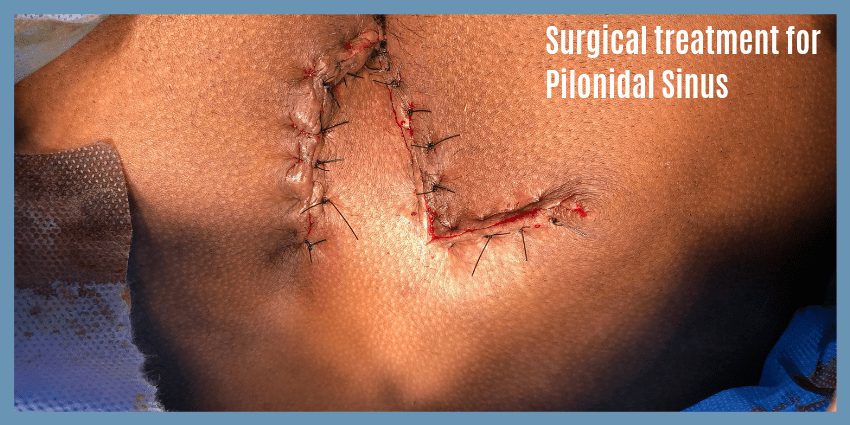
Surgical treatment for Pilonidal Sinus
In the case of large infected or recurring cysts, surgery is the best solution and it also has a very low recurrence rate.
The surgical treatment available today involves cutting and removing the sinus along with some of the skin around it and the two sides are stitched together.
Care and maintenance after surgery
- Ensure that the affected area is kept clean.
- Avoid wearing tight clothes and wear loose and comfortable clothes more often.
- Eat fibre rich foods to prevent constipation and avoiding straining while defecating.
- It is not advisable to do heavy lifting until the doctor says it is okay to do so.
- Do not drive vehicles especially motorcycles, bicycles for a few weeks or months depending on surgeon’s advice.
Even after the surgery, the surgical wound might heal very slowly. The primary reason for this is, the bottom region near the tail bone has not much of muscle fat. The second important reason is, the sinus is closer to the tail bone and the area is always under constant motion and stress. So it is imperative to take care of the surgical wound once the surgery has been completed.